Industry 4.0 Market: Smart Tech, Smarter Industry
Introduction
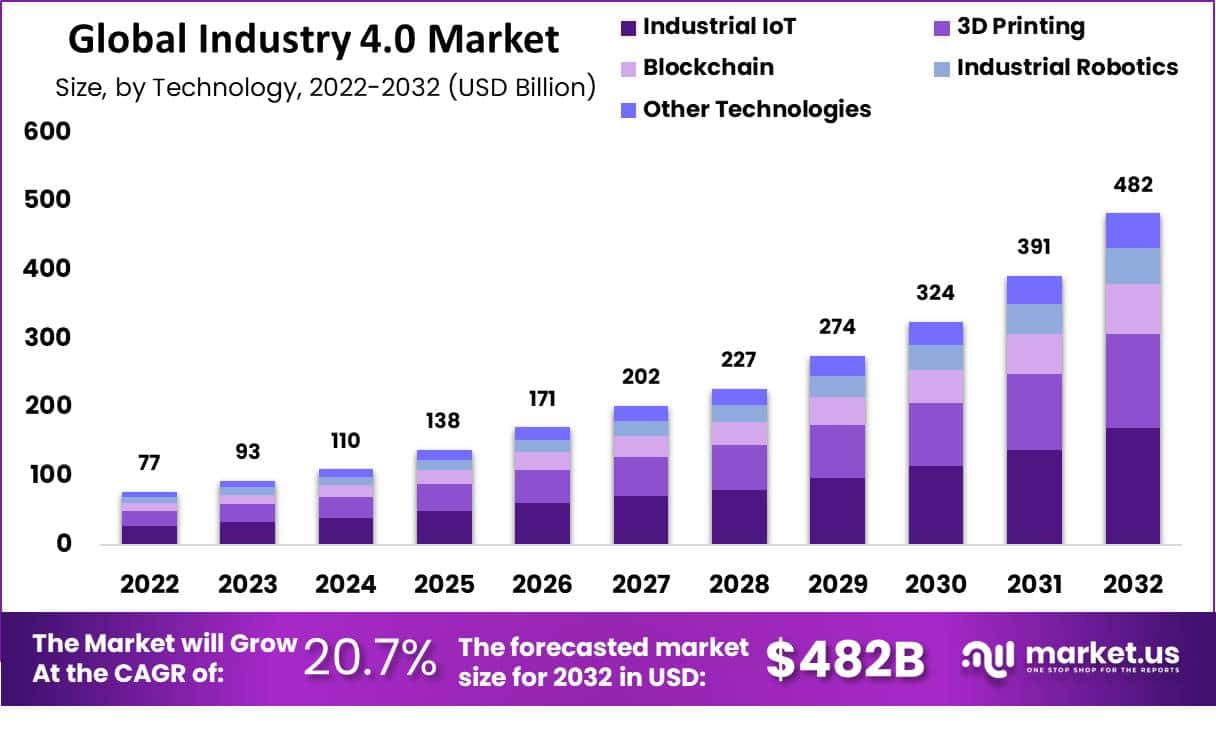
Industry 4.0 represents the fourth industrial revolution, marked by the integration of digital technologies into manufacturing processes. This shift is driven by advancements in artificial intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), big data, and automation. Growth factors include increased demand for efficiency, customization, and improved production quality. However, challenges such as high initial investment costs, cybersecurity threats, and the need for skilled labor pose significant hurdles. For new entrants, opportunities abound in niche markets, offering innovative solutions that cater to specific industry needs.
check in for more update on our webpage-https://market.us/report/industry-4-0-market/
Emerging Trends
IoT Integration: Seamless connectivity between machines and systems for real-time monitoring and optimization.
AI and Machine Learning: Enhancing decision-making processes and predictive maintenance in manufacturing.
Advanced Robotics: Implementation of collaborative robots (cobots) working alongside human workers.
3D Printing: Revolutionizing production with rapid prototyping and on-demand manufacturing.
Cyber-Physical Systems: Merging physical operations with digital technologies to create smart factories.
Top Use Cases
Predictive Maintenance: Utilizing data analytics to anticipate equipment failures and reduce downtime.
Smart Manufacturing: Automated and intelligent production lines that optimize resources and processes.
Supply Chain Management: Enhancing transparency and efficiency from raw materials to end products.
Quality Control: Implementing real-time inspection and monitoring systems to ensure product standards.
Energy Management: Optimizing energy usage across manufacturing processes to reduce costs and environmental impact.
Major Challenges
Cybersecurity Risks: Protecting interconnected systems from cyber-attacks and data breaches.
High Initial Costs: Significant investment required for new technologies and infrastructure.
Workforce Skill Gap: Need for skilled labor to manage and operate advanced technologies.
Integration Issues: Difficulty in merging new systems with existing legacy equipment.
Regulatory Compliance: Adhering to varying global standards and regulations in digital manufacturing.
Market Opportunity
Customization and Flexibility: Catering to the increasing demand for personalized products and agile production methods.
SME Adoption: Providing scalable and affordable solutions for small and medium-sized enterprises.
Sustainability Initiatives: Leveraging Industry 4.0 technologies to promote eco-friendly manufacturing practices.
Global Expansion: Tapping into emerging markets with tailored solutions to local industry needs.
Innovative Business Models: Developing new revenue streams through data-driven services and products.
Conclusion
Industry 4.0 is revolutionizing the manufacturing sector by integrating advanced digital technologies into production processes. While the journey comes with challenges like high costs and cybersecurity risks, the opportunities for growth and innovation are substantial. New entrants can find lucrative niches by offering tailored solutions, fostering a dynamic and competitive market landscape.
Recent Developments
Recent developments in Industry 4.0 include significant investments in AI-driven manufacturing, increased adoption of IoT devices for enhanced connectivity, and advancements in 5G technology enabling faster and more reliable industrial communication. Additionally, major companies are forming strategic partnerships to foster innovation and standardization within the industry, further accelerating the transformation towards smart manufacturing.
if you have inquiry make us-
location on 420 Lexington Avenue, Suite 300 New York City, NY 10170,
United States
phone
+1 718 618 4351 (International)
phone
+91 78878 22626 (Asia)
email
inquiry@market.us
Introduction
Industry 4.0 represents the fourth industrial revolution, marked by the integration of digital technologies into manufacturing processes. This shift is driven by advancements in artificial intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), big data, and automation. Growth factors include increased demand for efficiency, customization, and improved production quality. However, challenges such as high initial investment costs, cybersecurity threats, and the need for skilled labor pose significant hurdles. For new entrants, opportunities abound in niche markets, offering innovative solutions that cater to specific industry needs.
check in for more update on our webpage-https://market.us/report/industry-4-0-market/
Emerging Trends
IoT Integration: Seamless connectivity between machines and systems for real-time monitoring and optimization.
AI and Machine Learning: Enhancing decision-making processes and predictive maintenance in manufacturing.
Advanced Robotics: Implementation of collaborative robots (cobots) working alongside human workers.
3D Printing: Revolutionizing production with rapid prototyping and on-demand manufacturing.
Cyber-Physical Systems: Merging physical operations with digital technologies to create smart factories.
Top Use Cases
Predictive Maintenance: Utilizing data analytics to anticipate equipment failures and reduce downtime.
Smart Manufacturing: Automated and intelligent production lines that optimize resources and processes.
Supply Chain Management: Enhancing transparency and efficiency from raw materials to end products.
Quality Control: Implementing real-time inspection and monitoring systems to ensure product standards.
Energy Management: Optimizing energy usage across manufacturing processes to reduce costs and environmental impact.
Major Challenges
Cybersecurity Risks: Protecting interconnected systems from cyber-attacks and data breaches.
High Initial Costs: Significant investment required for new technologies and infrastructure.
Workforce Skill Gap: Need for skilled labor to manage and operate advanced technologies.
Integration Issues: Difficulty in merging new systems with existing legacy equipment.
Regulatory Compliance: Adhering to varying global standards and regulations in digital manufacturing.
Market Opportunity
Customization and Flexibility: Catering to the increasing demand for personalized products and agile production methods.
SME Adoption: Providing scalable and affordable solutions for small and medium-sized enterprises.
Sustainability Initiatives: Leveraging Industry 4.0 technologies to promote eco-friendly manufacturing practices.
Global Expansion: Tapping into emerging markets with tailored solutions to local industry needs.
Innovative Business Models: Developing new revenue streams through data-driven services and products.
Conclusion
Industry 4.0 is revolutionizing the manufacturing sector by integrating advanced digital technologies into production processes. While the journey comes with challenges like high costs and cybersecurity risks, the opportunities for growth and innovation are substantial. New entrants can find lucrative niches by offering tailored solutions, fostering a dynamic and competitive market landscape.
Recent Developments
Recent developments in Industry 4.0 include significant investments in AI-driven manufacturing, increased adoption of IoT devices for enhanced connectivity, and advancements in 5G technology enabling faster and more reliable industrial communication. Additionally, major companies are forming strategic partnerships to foster innovation and standardization within the industry, further accelerating the transformation towards smart manufacturing.
if you have inquiry make us-
location on 420 Lexington Avenue, Suite 300 New York City, NY 10170,
United States
phone
+1 718 618 4351 (International)
phone
+91 78878 22626 (Asia)
inquiry@market.us
Industry 4.0 Market: Smart Tech, Smarter Industry
Introduction
Industry 4.0 represents the fourth industrial revolution, marked by the integration of digital technologies into manufacturing processes. This shift is driven by advancements in artificial intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), big data, and automation. Growth factors include increased demand for efficiency, customization, and improved production quality. However, challenges such as high initial investment costs, cybersecurity threats, and the need for skilled labor pose significant hurdles. For new entrants, opportunities abound in niche markets, offering innovative solutions that cater to specific industry needs.
check in for more update on our webpage-https://market.us/report/industry-4-0-market/
Emerging Trends
IoT Integration: Seamless connectivity between machines and systems for real-time monitoring and optimization.
AI and Machine Learning: Enhancing decision-making processes and predictive maintenance in manufacturing.
Advanced Robotics: Implementation of collaborative robots (cobots) working alongside human workers.
3D Printing: Revolutionizing production with rapid prototyping and on-demand manufacturing.
Cyber-Physical Systems: Merging physical operations with digital technologies to create smart factories.
Top Use Cases
Predictive Maintenance: Utilizing data analytics to anticipate equipment failures and reduce downtime.
Smart Manufacturing: Automated and intelligent production lines that optimize resources and processes.
Supply Chain Management: Enhancing transparency and efficiency from raw materials to end products.
Quality Control: Implementing real-time inspection and monitoring systems to ensure product standards.
Energy Management: Optimizing energy usage across manufacturing processes to reduce costs and environmental impact.
Major Challenges
Cybersecurity Risks: Protecting interconnected systems from cyber-attacks and data breaches.
High Initial Costs: Significant investment required for new technologies and infrastructure.
Workforce Skill Gap: Need for skilled labor to manage and operate advanced technologies.
Integration Issues: Difficulty in merging new systems with existing legacy equipment.
Regulatory Compliance: Adhering to varying global standards and regulations in digital manufacturing.
Market Opportunity
Customization and Flexibility: Catering to the increasing demand for personalized products and agile production methods.
SME Adoption: Providing scalable and affordable solutions for small and medium-sized enterprises.
Sustainability Initiatives: Leveraging Industry 4.0 technologies to promote eco-friendly manufacturing practices.
Global Expansion: Tapping into emerging markets with tailored solutions to local industry needs.
Innovative Business Models: Developing new revenue streams through data-driven services and products.
Conclusion
Industry 4.0 is revolutionizing the manufacturing sector by integrating advanced digital technologies into production processes. While the journey comes with challenges like high costs and cybersecurity risks, the opportunities for growth and innovation are substantial. New entrants can find lucrative niches by offering tailored solutions, fostering a dynamic and competitive market landscape.
Recent Developments
Recent developments in Industry 4.0 include significant investments in AI-driven manufacturing, increased adoption of IoT devices for enhanced connectivity, and advancements in 5G technology enabling faster and more reliable industrial communication. Additionally, major companies are forming strategic partnerships to foster innovation and standardization within the industry, further accelerating the transformation towards smart manufacturing.
if you have inquiry make us-
location on 420 Lexington Avenue, Suite 300 New York City, NY 10170,
United States
phone
+1 718 618 4351 (International)
phone
+91 78878 22626 (Asia)
email
inquiry@market.us
0 Commentarii
0 Distribuiri
2K Views
0 previzualizare