How to Relieve Eye Pain: Tips and Treatments
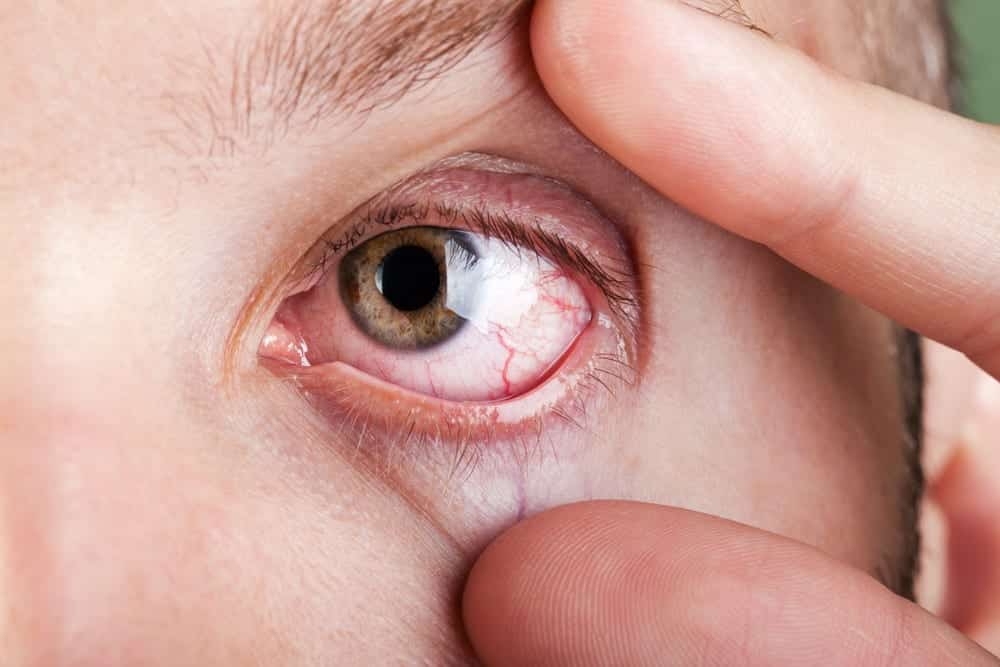
Eye pain is a common condition that can range from a minor irritation to a severe, debilitating problem. The causes of eye pain are varied, including infections, allergies, dry eyes, or more serious conditions like glaucoma. Knowing how to relieve eye pain effectively is essential to maintaining comfort and eye health. This article will provide an in-depth guide on how to manage and treat eye pain, including home remedies, over-the-counter treatments, and when to seek professional help. We’ll also cover key topics like pink eye treatment, eye irritation treatment, and the importance of scheduling an eye exam today for proper diagnosis and care.
Understanding Eye Pain
Eye pain can be broadly classified into two categories: surface pain and deeper pain.
Surface Pain
Surface pain typically affects the outer layers of the eye and can be caused by conditions such as:
- Pink Eye (Conjunctivitis): An infection or inflammation of the conjunctiva, the thin, transparent layer that covers the white part of the eye. Pink eye treatment usually involves pink eye medication like antibiotic eye drops or antihistamines.
- Dry Eyes: A condition where the eyes do not produce enough tears or the tears evaporate too quickly. Dry eyes can cause a gritty sensation, burning, and redness.
- Corneal Abrasions: Scratches on the cornea, the clear front surface of the eye, often caused by foreign objects or trauma.
- Allergies: Eye allergies can cause itching, redness, and swelling. They are often treated with antihistamine eye drops.
Deeper Pain
Deeper eye pain is felt within the eye and may be associated with more serious conditions, such as:
- Glaucoma: A condition that increases the pressure inside the eye, leading to optic nerve damage.
- Uveitis: Inflammation of the uvea, the middle layer of the eye, which can cause severe pain and vision changes.
- Sinusitis: Inflammation of the sinuses, which can cause pain around the eyes.
- Migraines: Severe headaches that can cause eye pain, sensitivity to light, and visual disturbances.
Understanding the type and cause of eye pain is crucial for determining the most appropriate treatment.
Home Remedies for Eye Pain Relief
Before seeking professional medical treatment, there are several home remedies you can try to relieve eye pain.
1. Cold Compress
A cold compress can help reduce swelling, redness, and discomfort associated with eye pain, especially in cases of pink eye or eye irritation.
- How to Apply: Soak a clean cloth in cold water, wring it out, and place it over your closed eyelids for 10-15 minutes. Repeat as needed.
- Benefits: Cold compresses help soothe itching, reduce inflammation, and provide relief from eye infections or allergic reactions.
2. Warm Compress
A warm compress is effective for treating conditions like blepharitis (inflammation of the eyelids) or styes, which can cause significant eye pain.
- How to Apply: Soak a clean cloth in warm water, wring it out, and place it over your closed eyelids for 5-10 minutes. Ensure the cloth is warm, not hot.
- Benefits: A warm compress can help unclog blocked oil glands in the eyelids, promote drainage, and reduce inflammation.
3. Artificial Tears
Artificial tears are over-the-counter eye drops that can help lubricate dry eyes and relieve discomfort caused by eye strain or dry eye syndrome.
- How to Use: Apply 1-2 drops in each eye as needed, typically every few hours. Follow the instructions on the packaging.
- Benefits: Artificial tears provide quick relief from dryness, burning, and the gritty feeling that often accompanies eye strain or environmental dryness.
4. Antihistamine Eye Drops
If your eye pain is due to allergies, antihistamine eye drops can provide quick relief from symptoms like itching, redness, and swelling.
- How to Use: Follow the dosage instructions on the packaging, usually 1-2 drops in each eye every 4-6 hours.
- Benefits: These drops reduce allergic reactions, providing relief from irritation and discomfort.
5. Proper Hydration
Dehydration can exacerbate eye pain, particularly if you suffer from dry eyes. Ensuring adequate hydration supports overall eye health.
- How to Maintain Hydration: Drink at least 8 glasses of water daily, and increase intake if you are in a dry or air-conditioned environment.
- Benefits: Staying hydrated helps maintain tear production and alleviate symptoms of dryness and irritation.
6. Blink Regularly
Blinking helps keep the eyes lubricated and free from irritants. Extended periods of focusing on screens or reading can reduce blinking frequency, leading to eye strain and discomfort.
- How to Practice Blinking: Make a conscious effort to blink more frequently, especially during prolonged screen use. Implement the 20-20-20 rule: Every 20 minutes, look at something 20 feet away for at least 20 seconds.
- Benefits: Regular blinking helps prevent dryness, reduces eye strain, and maintains proper eye moisture.
Over-the-Counter Treatments for Eye Pain
When home remedies are not enough, over-the-counter (OTC) treatments can provide additional relief for eye pain.
1. Lubricating Eye Drops
Lubricating eye drops, also known as artificial tears, can help relieve dryness and irritation caused by environmental factors, prolonged screen use, or dry eye syndrome.
- How to Use: Apply as needed throughout the day to keep your eyes moist and comfortable.
- Benefits: Lubricating eye drops provide immediate relief from dryness, reduce irritation, and help protect the eyes from further damage.
2. Antihistamine Eye Drops
For allergy-related eye pain, antihistamine eye drops can help reduce symptoms like itching, redness, and swelling.
- How to Use: Follow the instructions on the packaging, typically applying 1-2 drops in each eye as needed.
- Benefits: Antihistamine eye drops provide quick relief from allergic reactions, making them an effective option for treating eye pain caused by allergies.
3. Decongestant Eye Drops
Decongestant eye drops can help reduce redness and swelling caused by minor irritations or allergies.
- How to Use: Use these drops sparingly, as overuse can lead to rebound redness and worsening symptoms.
- Benefits: Decongestant eye drops can provide temporary relief from redness and swelling, making your eyes feel more comfortable.
4. Pain Relievers
Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, can help manage eye pain caused by inflammation or injury.
- How to Use: Follow the dosage instructions on the packaging, and consult your healthcare provider if you have any concerns.
- Benefits: Pain relievers can help reduce eye pain and discomfort, allowing you to focus on recovery.
Professional Treatment Options
While home remedies and OTC treatments can provide relief, some conditions require professional medical treatment. Knowing when to schedule an eye exam appointment is crucial for proper diagnosis and care.
1. Pink Eye Treatment
Pink eye, or conjunctivitis, is a common condition that can cause redness, itching, and discharge. Treatment depends on the cause:
- Bacterial Conjunctivitis: Pink eye treatment for bacterial infections typically involves antibiotic eye drops or ointments. It’s important to complete the full course of pink eye medication to prevent recurrence.
- Viral Conjunctivitis: This form of pink eye usually resolves on its own, but supportive treatments like cold compresses and artificial tears can help manage symptoms.
- Allergic Conjunctivitis: Treatment includes antihistamine or anti-inflammatory eye drops. Avoiding allergens is also important. For persistent cases, a consultation with an allergist or eye care specialist may be necessary.
2. Dry Eye Syndrome Treatment
Dry eye syndrome occurs when the eyes do not produce enough tears or when tears evaporate too quickly, leading to discomfort and potential vision problems.
- Artificial Tears: Over-the-counter lubricating eye drops can provide immediate relief from dryness. For more severe cases, prescription medications like cyclosporine (Restasis) or lifitegrast (Xiidra) may be recommended.
- Punctal Plugs: These tiny devices are inserted into the tear ducts to prevent tears from draining away too quickly, helping to keep the eyes moist.
- Environmental Adjustments: Using a humidifier, reducing screen time, and wearing sunglasses outdoors can also help manage symptoms and prevent dryness.
3. Corneal Abrasion Treatment
A corneal abrasion is a scratch or scrape on the cornea, often caused by foreign objects or trauma. It can lead to significant pain and discomfort.
- Antibiotic Eye Drops: To prevent infection and promote healing, antibiotic drops are often prescribed by a healthcare professional.
- Pain Management: Over-the-counter pain relievers can help alleviate discomfort. In some cases, your doctor may prescribe stronger medication.
- Follow-Up Care: Regular follow-up appointments are essential to monitor healing and address any potential complications, such as infections or corneal ulcers.
4. Glaucoma Treatment
Glaucoma is a group of eye conditions that damage the optic nerve, often due to high intraocular pressure. Early treatment is crucial to prevent vision loss.
- Eye Drops: Medications such as prostaglandin analogs, beta-blockers, or alpha agonists are commonly used to lower intraocular pressure.
- Laser Therapy: Procedures like laser trabeculoplasty can improve fluid drainage from the eye and help reduce pressure.
- Surgery: In advanced cases, surgical procedures may be necessary to create new drainage pathways or reduce pressure.
5. Eye Strain Treatment
Eye strain, also known as computer vision syndrome, is a common issue in today's digital age, especially among those who spend long hours in front of screens. Eye strain can cause discomfort, dryness, headaches, and blurred vision.
- Frequent Breaks: The 20-20-20 rule is highly effective: Every 20 minutes, look at something 20 feet away for at least 20 seconds. This helps reduce strain on the eyes.
- Proper Lighting: Ensure your work environment is well-lit to reduce glare on your screens. Position your screen so that light sources are not directly behind or in front of you.
- Screen Position: Your screen should be about an arm's length away from your eyes, with the top of the screen at or just below eye level. This helps maintain a comfortable viewing angle and reduces strain.
- Blue Light Filters: Use blue light filters on your devices or wear blue light-blocking glasses to minimize the impact of blue light, which can contribute to eye strain.
- Artificial Tears: If your eyes feel dry, using lubricating eye drops can provide relief. Be sure to blink regularly, especially when focusing on digital screens.
6. Uveitis Treatment
Uveitis is an inflammation of the uvea, the middle layer of the eye, and can cause severe pain, redness, and vision changes. It requires prompt medical attention.
- Steroid Eye Drops: These are commonly prescribed to reduce inflammation. In more severe cases, oral or injectable steroids may be necessary.
- Immunosuppressive Drugs: If uveitis is related to an underlying autoimmune condition, immunosuppressive medications may be prescribed to control inflammation.
- Close Monitoring: Regular eye care appointments are essential for monitoring the condition and adjusting treatment as needed to prevent complications such as glaucoma or cataracts.
7. Sinusitis-Related Eye Pain Treatment
Sinusitis, an inflammation of the sinuses, can cause pain around the eyes due to pressure in the sinus cavities. Treating sinusitis can relieve this type of eye pain.
- Decongestants: Over-the-counter decongestants can help reduce sinus pressure, alleviating pain around the eyes.
- Saline Nasal Sprays: These sprays can help clear nasal passages, reducing congestion and sinus pressure.
- Warm Compresses: Applying a warm compress to the affected area can help relieve sinus pressure and reduce eye pain.
- Antibiotics: If sinusitis is caused by a bacterial infection, your doctor may prescribe antibiotics to clear the infection.
When to Seek Professional Help
While many cases of eye pain can be managed with home remedies and over-the-counter treatments, certain situations require professional medical attention. Knowing when to schedule an eye exam today can prevent serious complications and ensure proper treatment.
1. Persistent or Severe Pain
If you experience persistent or severe eye pain that does not improve with home treatment, it’s important to see a doctor. This could indicate a more serious underlying condition that requires medical intervention.
2. Vision Changes
Sudden changes in vision, such as blurriness, double vision, or loss of vision, should be evaluated by an eye care professional immediately. These symptoms could indicate a serious issue like glaucoma, retinal detachment, or a stroke.
3. Eye Injury
If you have sustained an eye injury, whether from trauma, a foreign object, or exposure to chemicals, seek medical attention promptly. Eye injuries can lead to infections, scarring, or vision loss if not treated properly.
4. Redness and Discharge
If your eye is red and producing a significant amount of discharge, it could be a sign of an infection like conjunctivitis. Pink eye treatment with appropriate pink eye medication is necessary to prevent the spread of the infection and to alleviate symptoms.
5. Recurrent Eye Pain
If you experience recurrent episodes of eye pain, it’s important to schedule an eye care appointment. Recurrent pain could indicate an underlying condition that needs to be diagnosed and treated to prevent further complications.
Preparing for Your Eye Care Appointment
When you’re experiencing eye pain and decide to see a doctor, preparing for your eye exam appointment can help ensure you get the most out of your visit.
1. Document Symptoms
Keep a detailed record of your symptoms, including when they started, how they have progressed, and any triggers you’ve noticed. This information can help your doctor make an accurate diagnosis.
2. List Medications
Bring a list of any medications you are currently taking, including over-the-counter treatments and supplements. Some medications can have side effects that affect the eyes, so it’s important to discuss these with your doctor.
3. Note Medical History
Be prepared to discuss your medical history, including any previous eye conditions, surgeries, or chronic illnesses. Certain conditions, such as diabetes or autoimmune diseases, can increase the risk of eye problems.
4. Prepare Questions
Think about any questions or concerns you want to address during your appointment. For example, you may want to ask about the best treatment options for your condition, how to prevent future eye pain, or what lifestyle changes could improve your eye health.
5. Bring Eyewear
If you wear glasses or contact lenses, bring them with you to your appointment. Your eye doctor may need to evaluate your prescription and check your vision with your current eyewear.
Conclusion
Eye pain can be uncomfortable and concerning, but with the right knowledge and treatment, most cases can be effectively managed. Whether you’re dealing with minor irritation or more serious pain, there are a variety of home remedies, over-the-counter treatments, and professional medical options available. Understanding the causes of your eye pain and knowing when to seek professional help are crucial steps in maintaining your eye health.
For conditions like pink eye, appropriate pink eye treatment with the right pink eye medication can quickly alleviate symptoms. Regular eye care appointments and prompt eye exams are essential for preventing and treating more serious issues. By staying informed and proactive, you can ensure that your eyes remain healthy and pain-free.
- Industry
- Art
- Causes
- Crafts
- Dance
- Drinks
- Film
- Fitness
- Food
- Jogos
- Gardening
- Health
- Início
- Literature
- Music
- Networking
- Outro
- Party
- Religion
- Shopping
- Sports
- Theater
- Wellness
- News


