Understanding Multi-Access Edge Computing: A Comprehensive Overview
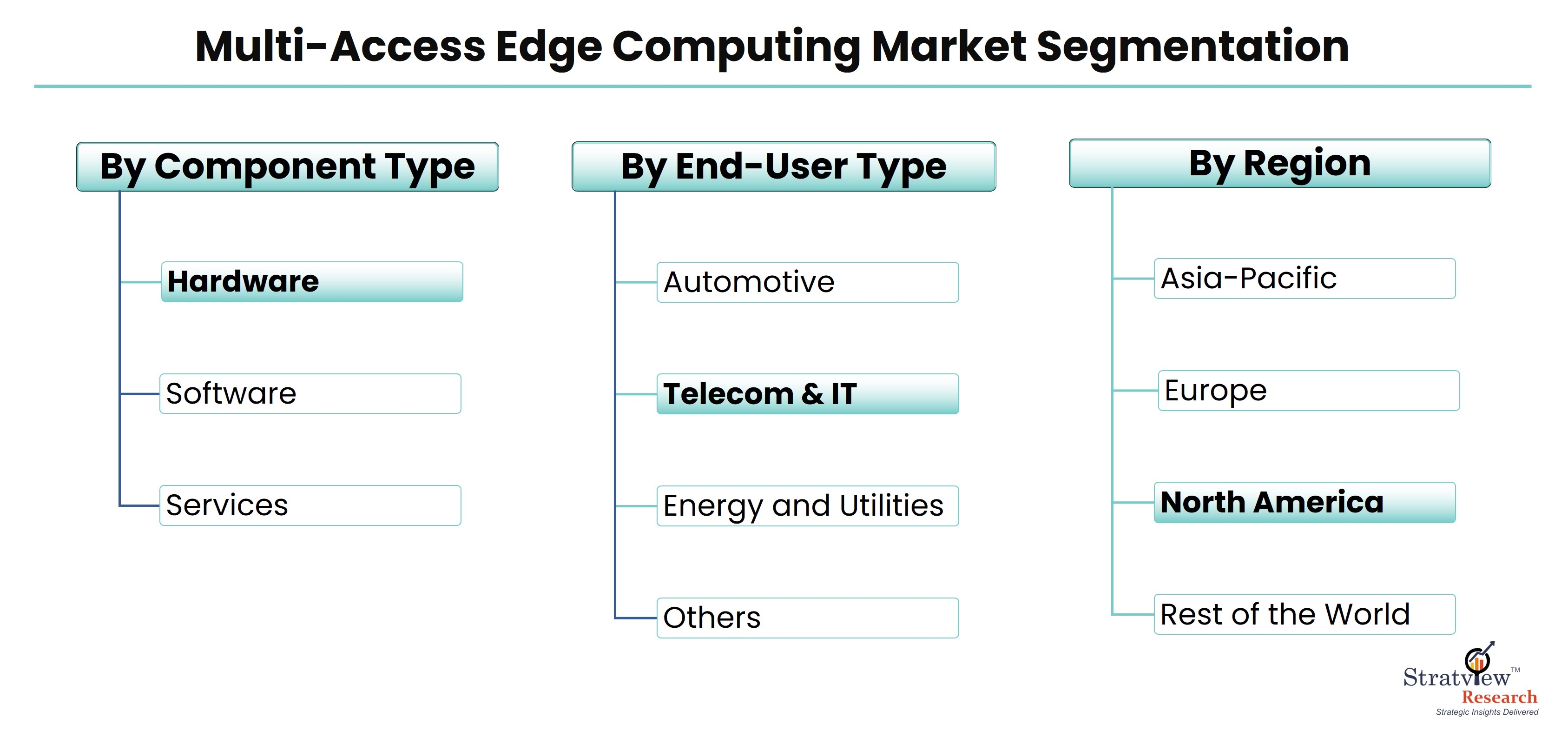
Multi-Access Edge Computing (MEC) is a transformative technology that brings computation and data storage closer to the end user, addressing the latency and bandwidth challenges of traditional cloud computing. By leveraging the edge of the network, MEC enhances performance and efficiency, making it a pivotal component in the evolving landscape of digital connectivity.
According to Stratview Research, the multi-access edge computing market was estimated at USD 2.27 billion in 2022 and is likely to grow at a CAGR of 48.96% during 2023-2028 to reach USD 25.01 billion in 2028.
1. What is Multi-Access Edge Computing? Multi-Access Edge Computing is an architectural framework that integrates cloud computing capabilities at the edge of the network. This means that instead of processing data in centralized cloud data centers, MEC brings computing resources closer to where data is generated and consumed. This approach significantly reduces latency, improves speed, and enhances the overall user experience.
2. Key Benefits of Multi-Access Edge Computing - Multi-Access Edge Computing offers several advantages over traditional cloud computing models. Firstly, it reduces latency by processing data closer to the end user, which is crucial for applications requiring real-time responses, such as autonomous vehicles, augmented reality (AR), and virtual reality (VR). Secondly, Multi-Access Edge Computing alleviates network congestion by offloading traffic from central data centers to edge nodes, thus optimizing bandwidth usage. Additionally, Multi-Access Edge Computing enhances data security and privacy by processing sensitive information locally rather than transmitting it over long distances.
3. Applications and Use Cases The versatility of Multi-Access Edge Computing makes it applicable across various sectors. In smart cities, Multi-Access Edge Computing enables efficient traffic management and public safety systems by processing data from sensors and cameras in real-time. In the industrial sector, it supports Industry 4.0 initiatives by enhancing the performance of IoT devices and automation systems. For the entertainment industry, Multi-Access Edge Computing provides the low-latency required for seamless AR and VR experiences. Furthermore, Multi-Access Edge Computing plays a crucial role in 5G networks by supporting the high-speed, low-latency requirements of next-generation applications.
4. Integration with 5G One of the most significant drivers of Multi-Access Edge Computing adoption is its integration with 5G technology. The ultra-low latency and high data rates of 5G networks complement Multi-Access Edge Computings capabilities, enabling advanced applications such as smart manufacturing, connected healthcare, and immersive media experiences. Together, Multi-Access Edge Computing and 5G create a robust infrastructure for handling the growing demands of digital services and applications.
5. Challenges and Considerations Despite its benefits, Multi-Access Edge Computing also faces challenges. Deploying and managing edge infrastructure requires significant investment and technical expertise. Ensuring interoperability between different edge devices and systems can be complex, and addressing security concerns at multiple edge locations is critical.
In conclusion, Multi-Access Edge Computing represents a significant advancement in network architecture, offering enhanced performance, reduced latency, and improved efficiency. As industries continue to embrace digital transformation, Multi-Access Edge Computing will play a crucial role in enabling next-generation applications and services, shaping the future of connectivity and computing.
- Industry
- Art
- Causes
- Crafts
- Dance
- Drinks
- Film
- Fitness
- Food
- Oyunlar
- Gardening
- Health
- Home
- Literature
- Music
- Networking
- Other
- Party
- Religion
- Shopping
- Sports
- Theater
- Wellness
- News


