Unlocking Innovation: Exploring the Diverse World of Push Button Technologies
Introduction
Push button technologies are the unsung heroes of modern interaction, seamlessly connecting us with technology and machinery through simple yet effective mechanisms. Whether it's a doorbell or an industrial control system, these mechanisms complete electrical circuits upon being pressed, initiating specific actions or responses.
From basic momentary switches to advanced variants with illuminated indicators and integrated electronics, electrical push buttons cater to diverse needs across industries. And as technology gets better, new features like touch sensitivity or feedback make push buttons even more useful and important for how we interact with machines.
In this introduction to push button technologies, we'll explore the various types, applications, and other information. Whether you're just interested in how things work or you're a pro in the field, knowing about push button technologies is super important for using them well in our connected world.
The Evolution of Push Button Technology
Push button technology emerged as simple mechanical switches, requiring physical force to activate electrical circuits. These early designs were basic yet effective, serving purposes like turning lights on and off or ringing doorbells. However, as industries demanded more sophisticated control mechanisms, push button technology evolved rapidly.
The advent of electronic components ushered in a new era for push buttons, introducing features like illuminated indicators, tactile feedback, and customizable functionality. These advancements not only enhanced user experience but also expanded the scope of push button applications across various sectors, including automotive, industrial automation, and consumer electronics.
In recent years, the integration of digital technology has propelled push button technology to new heights. Capacitive touch sensors, for instance, enable touch-sensitive buttons without the need for physical pressure, offering sleek and intuitive interfaces in smartphones and touch panels. Furthermore, wireless connectivity and smart functionality have transformed push buttons into integral components of interconnected systems, enabling remote control and automation in smart homes and IoT devices.
Looking ahead, the evolution of push button technology shows no signs of slowing down. With ongoing research and development, we can expect even more innovations, such as gesture recognition, augmented reality interfaces, and seamless integration with artificial intelligence. As an Electrical Products Specialist, I'm excited to witness and contribute to the continued evolution of push button technology, shaping the future of human-machine interaction.
Different Types of Push Button Technologies
Here's a comprehensive overview of the different types of push button technologies:
-
Mechanical Push Buttons: These are the traditional push buttons that rely on physical force to activate. When the button is pressed, it completes an electrical circuit, triggering a specific action. Mechanical push buttons are commonly used in applications like doorbells, elevator controls, and basic on/off switches.
-
Momentary Push Buttons: These switches come in two variants: Normally open and Normally closed., momentary switches only remain in the activated state while they are being pressed. They revert to their original state when released. These are commonly found in devices where temporary activation is needed, such as computer mice, remote controls, and game controllers.
-
Toggle Switches: Unlike momentary switches/push buttons, toggle switches maintain their state after being activated until they are toggled again. They are often used for on/off functions in appliances, lighting systems, and electronic devices.
-
Illuminated Push Buttons: These push buttons feature built-in lighting elements, such as LEDs, to provide visual feedback or indication of their status. They are commonly used in control panels, machinery, and automotive applications where visibility in low-light conditions is important.
-
Keylock Push Buttons: Keylock push buttons require a key to activate, providing an extra layer of security to prevent unauthorized access or operation. They are frequently used in security systems, industrial equipment, and machinery that require restricted access.
-
Capacitive Touch Buttons: Capacitive touch buttons detect the presence of a conductive object, such as a finger, without the need for physical pressure. They offer a sleek and modern interface, commonly found in smartphones, touchscreens, and industrial panels.
-
Haptic Feedback Push Buttons: These buttons provide tactile feedback, such as a vibration or click sensation, to simulate the feeling of pressing a physical button. Haptic feedback enhances the user experience and is often used in gaming controllers, virtual reality systems, and touchscreen devices.
-
Wireless Push Buttons: With advancements in wireless technology, push buttons can now be connected wirelessly to devices or systems. Wireless push buttons enable remote control and automation, making them ideal for smart home applications, IoT devices, and industrial automation.
-
Integrated Electronics Push Buttons: Some push buttons incorporate integrated electronics, such as microcontrollers or sensors, to offer advanced functionalities. These can include programmable actions, gesture recognition, or compatibility with smart home ecosystems.
How Push Button Works?
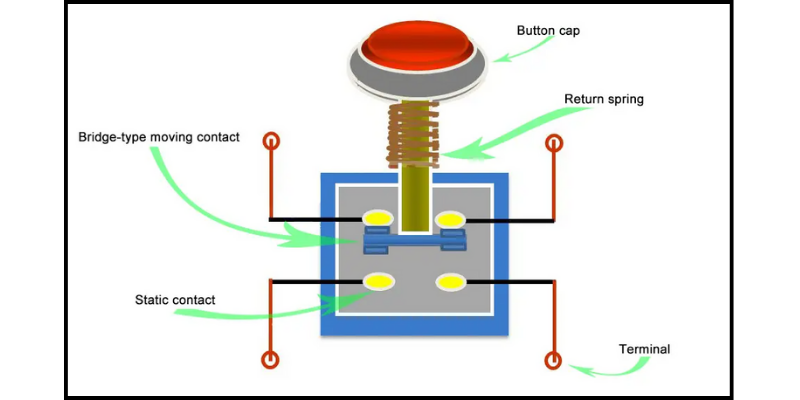
Here's an informative description from an expert perspective on how electrical push buttons work:
Electrical push buttons serve as fundamental components in control systems across various industries, facilitating the initiation of specific functions or operations with a simple press. At their core, these push buttons operate on the principle of completing an electrical circuit to trigger a desired action.
When a user presses the button, it actuates a mechanism that physically closes an electrical circuit, allowing current to flow through. This completion of the circuit sends a signal to the associated device or system, prompting it to perform the intended function.
In a basic momentary push button, the circuit is only closed while the button is being pressed, and it returns to its original state when released. On the other hand, toggle switches maintain their state after activation until toggled again.
Mechanically, push buttons typically consist of a button cap, a plunger or actuator, and a contact block containing electrical contacts. When the button is pressed, the plunger moves to make contact with the electrical contacts, closing the circuit.
Depending on the application, push buttons may incorporate additional features such as illumination for visibility in low-light environments, keylock mechanisms for security purposes, or integrated electronics for advanced functionalities like digital input or wireless communication.
Understanding how electrical push buttons work is essential for designing reliable control systems and ensuring proper functionality in various industrial and commercial applications. Expert knowledge in selecting the appropriate type of push button based on the specific requirements of the application can optimize performance and enhance operational efficiency.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Push Button technologies
Here are the advantages and disadvantages of electrical push buttons:
Advantages:
-
Simplicity: Push buttons are intuitive and easy to use, requiring only a simple press to activate.
-
Reliability: Push buttons are robust and durable, with mechanical designs that ensure consistent performance over time.
-
Versatility: Push buttons come in various types and configurations to suit different applications and user preferences.
-
Instantaneous Feedback: Push buttons provide immediate tactile or visual feedback upon activation, confirming the action to the user.
-
Safety: Start Stop Push buttons can be designed with features like keylocks or guarded covers to prevent accidental activation, enhancing safety in industrial settings.
-
Cost-Effectiveness: Push buttons are often more cost-effective compared to other types of control interfaces, making them a preferred choice for many applications.
Disadvantages:
-
Limited Functionality: Push buttons typically offer simple on/off or momentary control functions, lacking the complexity of touchscreens or digital interfaces.
-
Space Requirements: Push buttons may require more physical space compared to touch-sensitive controls or membrane keypads, especially when multiple buttons are needed.
-
Wear and Tear: Mechanical push buttons may experience wear and tear over time, leading to eventual degradation in performance and reliability.
-
Environmental Sensitivity: Some push buttons may be susceptible to environmental factors like moisture, dust, or temperature fluctuations, impacting their longevity and functionality.
-
Limited Feedback Options: While push buttons provide immediate feedback upon activation, the feedback options are limited compared to digital interfaces, which can display detailed information or status updates.
How to Choose the Perfect Push Buttons?
-
Identify Your Application: First, determine the specific application for which you need the push button. Is it for a simple on/off function, or do you require additional features like illumination or keylock capability?
-
Consider Environmental Factors: Think about the environment in which the push button will be installed. Will it be exposed to moisture, dust, or extreme temperatures? Choose a push button with the appropriate environmental ratings to ensure durability and reliability.
-
Select the Type: There are various types of push buttons available, such as momentary, toggle, illuminated, and keylock. Choose the type that best suits your application and user preferences.
-
Size and Mounting: Consider the size and mounting options of the push button. Ensure that it fits comfortably in the designated space and that the mounting style aligns with your installation requirements.
-
Feedback Mechanism: Decide on the desired feedback mechanism. Do you prefer tactile feedback, visual indicators, or both? Choose a push button that provides the feedback you need for ease of use.
-
Quality and Reliability: Look for push buttons from reputable manufacturers known for their quality and reliability. Investing in a high-quality push button ensures long-term performance and minimizes the risk of malfunctions.
-
Compatibility: Check compatibility with your existing electrical system or control panel. Ensure that the push button's electrical ratings and connections match your system requirements to avoid compatibility issues.
-
Budget: Consider your budget constraints when choosing a push button. While quality is essential, there are options available to suit various budgets without compromising on performance.
- Industry
- Art
- Causes
- Crafts
- Dance
- Drinks
- Film
- Fitness
- Food
- Juegos
- Gardening
- Health
- Home
- Literature
- Music
- Networking
- Other
- Party
- Religion
- Shopping
- Sports
- Theater
- Wellness
- News


