Gingivitis, a common and often overlooked dental issue, is the inflammation of the gums caused by the accumulation of plaque—a sticky film of bacteria—on the teeth. While gingivitis is a mild and reversible condition, it can progress to more severe forms of gum disease if left untreated. This blog post aims to shed light on gingivitis, its causes, symptoms, and, most importantly, effective treatment options to maintain optimal oral health.
Causes and Symptoms of Gingivitis
Before delving into treatment options, it's crucial to understand the causes and symptoms of gingivitis. Poor oral hygiene is the primary culprit, as it accumulates plaque along the gumline. Plaque is a breeding ground for bacteria that can irritate the gums, causing inflammation. The best gingivitis treatment from Ontario, is the solution to your problem.
Common causes of gingivitis include:
- Inadequate brushing and flossing.
- Smoking.
- Certain medical conditions.
- Hormonal changes (such as during pregnancy or menstruation).
- Specific medications that reduce saliva flow.
Recognizing the symptoms early on is critical to preventing the progression of gingivitis. These symptoms may include:
- Red, swollen gums: Inflammation is a hallmark sign of gingivitis. Healthy gums should appear pink and firm, but gingivitis can make them red and puffy.
- Bleeding gums: One of the most noticeable symptoms is bleeding while brushing or flossing. Healthy gums should not bleed during routine oral care.
- Bad breath: The bacteria in plaque release toxins that contribute to unpleasant breath. Persistent bad breath may be an indication of gingivitis.
- Tender or sensitive gums: Gingivitis can make the gums more sensitive, causing discomfort during brushing or eating.
Now that we understand the signs and causes let's explore effective treatment options for gingivitis.
Gingivitis Treatment Options
- Improved Oral Hygiene Practices: The foundation of gingivitis treatment lies in improving oral hygiene. Dentists recommend brushing teeth at least twice a day using fluoride toothpaste. Regular flossing is also essential to remove plaque and debris between the teeth. Using an antiseptic mouthwash can also help kill bacteria and reduce plaque.
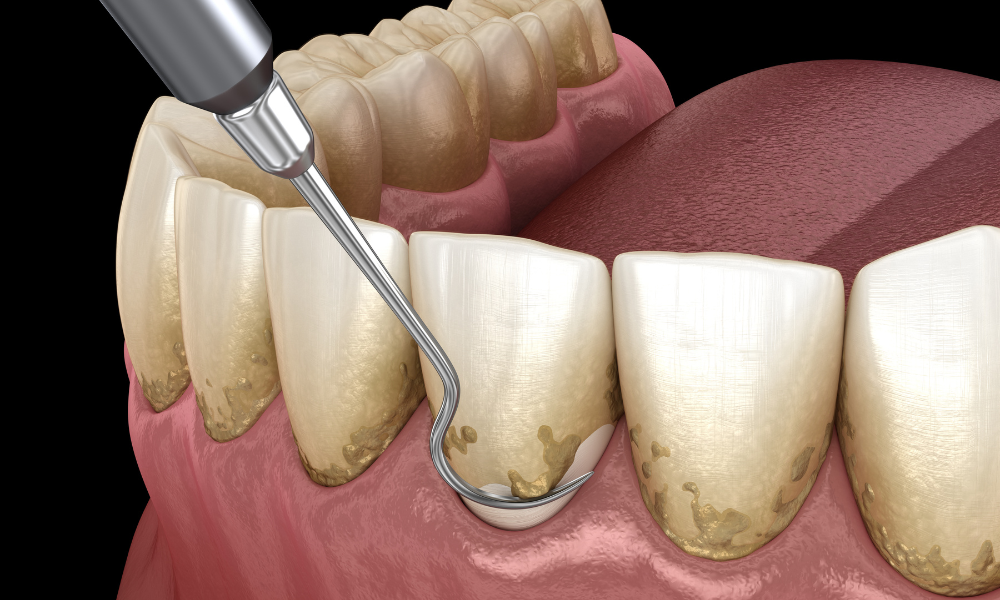
- Professional Dental Cleanings: Regular dental check-ups and professional cleanings are critical for managing and preventing gingivitis. Dental professionals can remove hardened plaque (tartar or calculus) that cannot be eliminated through regular brushing and flossing. Professional cleanings also provide an opportunity to assess oral health and promptly address concerns.
- Antibacterial Mouthwashes: Dentists may recommend antibacterial mouthwashes containing chlorhexidine or essential oils. These mouthwashes can help reduce bacteria in the mouth and alleviate gingivitis symptoms. However, using them as directed is essential, as prolonged use may lead to teeth staining.
- Topical or Oral Antibiotics: In some cases, dentists may prescribe topical or oral antibiotics to control bacterial infection and inflammation. These medications are typically used for more severe cases of gingivitis and are administered under professional supervision.
- Lifestyle Changes: Addressing factors contributing to gingivitis is crucial for effective treatment. Quitting smoking, maintaining a healthy diet, and managing stress can positively impact oral health and prevent the recurrence of gingivitis.
- Managing Underlying Conditions: Addressing those underlying factors is essential if gingivitis is linked to specific medical conditions or hormonal changes. This may involve collaboration between the dentist and other healthcare professionals to ensure comprehensive care.
Gingivitis, if detected and treated early, is a reversible condition. Individuals can effectively manage and prevent gingivitis by prioritizing good oral hygiene practices, seeking regular professional cleanings, and making necessary lifestyle adjustments. Ignoring the signs and symptoms of gingivitis can lead to more severe forms of gum disease, which may result in irreversible damage to the gums and supporting structures of the teeth. Remember, a healthy smile starts with a commitment to consistent and thorough oral care.