https://www.glsun.com/article-p109-optical-amplifier-edfa-for-wdm-system.html
What's EDFA?
Erbium-Doped Fiber Amplifier (EDFA) is an optical amplifier used in the C-band and L-band, where the loss of telecom optical fibers becomes lowest in the entire optical telecommunication wavelength bands. It is used in the telecommunications field and in various types of research fields. An EDFA is "doped" with a material called erbium. Optical amplifiers can directly amplify optical signals without converting the signals into electrical signals before amplification, which is also the most prominent function and is an important optical component in long-distance optical communication.
EDFA has been widely used in DWDM system, usually used to compensate the link loss in long-distance optical communication. The most important feature is to amplify multiple optical signals at the same time and can be easily combined with Wavelength division multiplexing (WDM) technology. The common bands of EDFA are C-band and L-band. Wavelength division multiplexing (WDM) techniques combined with erbium-doped fiber amplifier (EDFA) increases the capacity of light wave transmission, provides high capacity and improves flexibility of optical network technology.
EDFA Working Principle
EDFA works on the principle of stimulating the emission of photons. With EDFA, an erbium-doped optical fiber at the core is pumped with light from laser diodes. The erbium-doped fiber (EDF) is at the core of EDFA technology, which is a conventional silica fiber doped with Erbium. It is a conventional silica fiber doped with erbium. When the Erbium is illuminated with light energy at a suitable wavelength (either 980nm or1480nm), it is excited to a long lifetime intermediate state, then it decays back to the ground state by emitting light within the 1525-1565nm band. When the light energy already exists within the 1525-2565nm band, for example due to a signal channel passing through the EDF, then this stimulates the decay process, resulting in additional light energy.
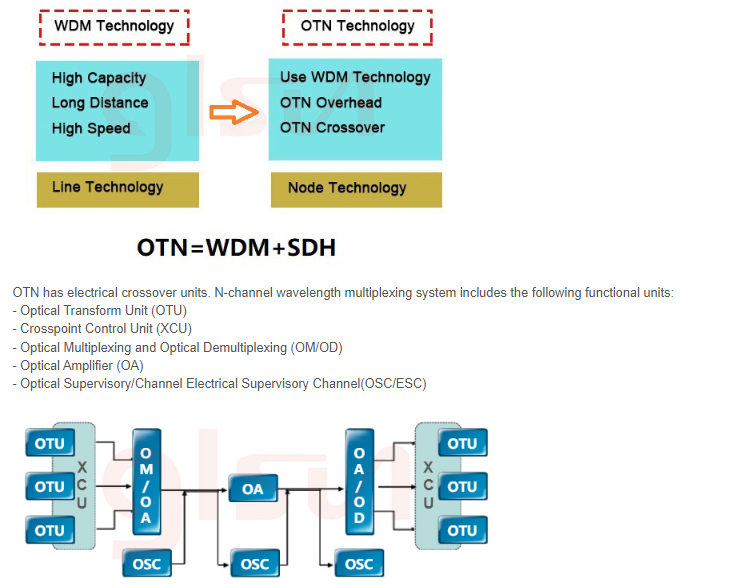
Baisc configuration of EDFA
EDFA configuration is mainly composed of erbium-doped fiber (EDF), pump laser, coupler, WDM, optical isolator, gain flattening filter (GFF), variable optical attenuators (VOA) and photodetector (PD). In principle, EDFAs can be designed such that pump energy propagates in the same direction as the signal (forward pumping), the opposite direction to the signal (backward pumping), or both direction together.
Coupler: the optical power is branched and transmitted according to a certain proportion, usually using the melting taper process.
WDM: a passive optical device that mixes up the input optical signal and the light wave output from the pump light source, generally using a wavelength division multiplexer(WDM).
https://www.glsun.com/article-p109-optical-amplifier-edfa-for-wdm-system.html
https://www.glsun.com/article-p109-optical-amplifier-edfa-for-wdm-system.html
What's EDFA?
Erbium-Doped Fiber Amplifier (EDFA) is an optical amplifier used in the C-band and L-band, where the loss of telecom optical fibers becomes lowest in the entire optical telecommunication wavelength bands. It is used in the telecommunications field and in various types of research fields. An EDFA is "doped" with a material called erbium. Optical amplifiers can directly amplify optical signals without converting the signals into electrical signals before amplification, which is also the most prominent function and is an important optical component in long-distance optical communication.
EDFA has been widely used in DWDM system, usually used to compensate the link loss in long-distance optical communication. The most important feature is to amplify multiple optical signals at the same time and can be easily combined with Wavelength division multiplexing (WDM) technology. The common bands of EDFA are C-band and L-band. Wavelength division multiplexing (WDM) techniques combined with erbium-doped fiber amplifier (EDFA) increases the capacity of light wave transmission, provides high capacity and improves flexibility of optical network technology.
EDFA Working Principle
EDFA works on the principle of stimulating the emission of photons. With EDFA, an erbium-doped optical fiber at the core is pumped with light from laser diodes. The erbium-doped fiber (EDF) is at the core of EDFA technology, which is a conventional silica fiber doped with Erbium. It is a conventional silica fiber doped with erbium. When the Erbium is illuminated with light energy at a suitable wavelength (either 980nm or1480nm), it is excited to a long lifetime intermediate state, then it decays back to the ground state by emitting light within the 1525-1565nm band. When the light energy already exists within the 1525-2565nm band, for example due to a signal channel passing through the EDF, then this stimulates the decay process, resulting in additional light energy.
Baisc configuration of EDFA
EDFA configuration is mainly composed of erbium-doped fiber (EDF), pump laser, coupler, WDM, optical isolator, gain flattening filter (GFF), variable optical attenuators (VOA) and photodetector (PD). In principle, EDFAs can be designed such that pump energy propagates in the same direction as the signal (forward pumping), the opposite direction to the signal (backward pumping), or both direction together.
Coupler: the optical power is branched and transmitted according to a certain proportion, usually using the melting taper process.
WDM: a passive optical device that mixes up the input optical signal and the light wave output from the pump light source, generally using a wavelength division multiplexer(WDM).
https://www.glsun.com/article-p109-optical-amplifier-edfa-for-wdm-system.html