Pinpoint Pupils: What They Mean and When to Seek Help
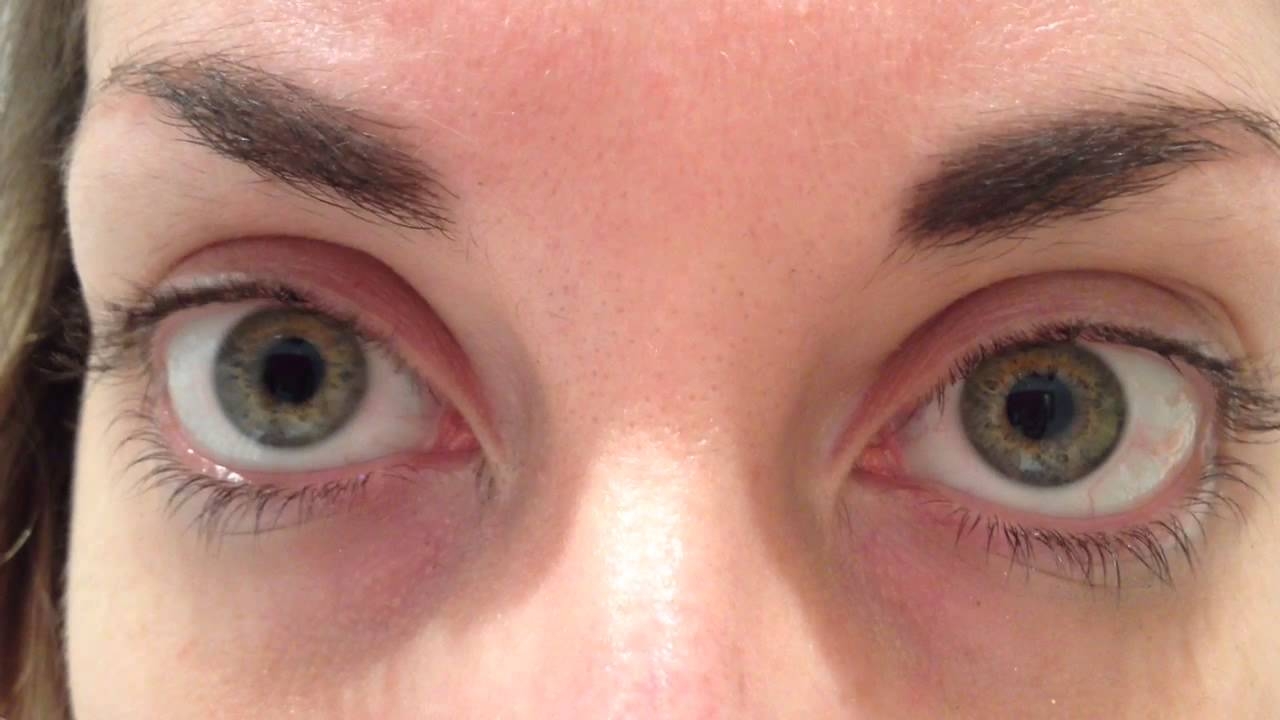
Our eyes often reveal more than we realise. They reflect emotions, health conditions, and sometimes serious medical issues. One noticeable change that can indicate underlying problems is having pinpoint pupils. This condition, though sometimes temporary or harmless, can also be a sign of something that requires urgent attention.
What Is a Pinpoint Pupil?
A pinpoint pupil refers to a pupil that is abnormally small in size. Medically, this condition is known as miosis. While the normal pupil size changes depending on lighting and other factors, pinpoint pupils remain constricted regardless of the surrounding brightness. They appear as tiny dots in the centre of the eye, which can affect how well a person sees in low light.
Although both pupils may appear equally small, in some cases, the effect may occur in only one eye. When this happens without an obvious reason, it's essential to investigate further.
Causes of Pinpoint Pupils
There are multiple potential causes behind pinpoint pupils. Understanding them helps in determining whether the condition is benign or dangerous.
1. Opioid Use or Overdose
One of the most recognised causes of pinpoint pupils is opioid consumption. Drugs such as morphine, heroin, oxycodone, and fentanyl are known to trigger this reaction. In overdose cases, pinpoint pupils may be accompanied by slow breathing and unconsciousness, forming a medical emergency known as the "opioid overdose triad".
2. Exposure to Certain Toxins or Chemicals
Some insecticides and nerve agents, such as organophosphates, can lead to pinpoint pupils. These substances interfere with the nervous system, causing abnormal reactions in the body, including pupil constriction.
3. Neurological Conditions
A pinpoint pupil can also be a sign of neurological impairment. Conditions like brain haemorrhages, tumours pressing on specific brain structures, or strokes affecting the brainstem can cause this response. When linked to such issues, the affected individual may show additional symptoms such as confusion, weakness, or trouble speaking.
4. Medications
Besides opioids, some eye drops used to treat glaucoma and medications for high blood pressure or psychiatric conditions may cause pupil constriction. It’s important to track any new prescriptions that coincide with the appearance of pinpoint pupils.
5. Infections or Inflammation
Infections like neurosyphilis or inflammation such as Horner's syndrome may also produce this symptom. These conditions are rare but require detailed investigation and specialist treatment.
Associated Symptoms to Watch For
While a pinpoint pupil itself might seem minor, it's crucial to consider other symptoms that could accompany it. Here are a few warning signs that may suggest a more serious problem:
-
Slurred speech
-
Trouble breathing
-
Sudden confusion or memory loss
-
Severe headaches
-
Unresponsiveness or unconsciousness
-
Vision disturbances
These signs could indicate stroke, poisoning, or drug overdose—conditions where time is of the essence.
When Should You Seek Medical Help?
It is always wise to seek professional help if you or someone you know has unusually small pupils without a clear cause. In particular, seek emergency care if:
-
The person is unconscious or difficult to wake
-
There are signs of drug overdose
-
Symptoms appear after exposure to unknown chemicals
-
Vision becomes suddenly impaired
-
Neurological symptoms such as numbness or speech problems develop
In such cases, early diagnosis and treatment can make a significant difference.
Diagnosis and Tests
When a person presents with a pinpoint pupil, doctors conduct a thorough examination to identify the underlying cause. Some of the common diagnostic steps include:
-
Reviewing medical history and current medications
-
Checking for signs of drug use or withdrawal
-
Neurological examination
-
Blood and urine tests
-
Imaging tests such as CT or MRI scans
The goal is to determine whether the cause is temporary or life-threatening, and to guide treatment accordingly.
Treatment Options
Treatment depends entirely on the cause of the pinpoint pupils. Here are some examples:
-
Opioid overdose: Administration of naloxone, a life-saving drug that reverses opioid effects.
-
Chemical exposure: Detoxification or use of antidotes for specific poisons.
-
Neurological issues: Surgery, medication, or rehabilitation depending on the nature of the problem.
-
Medication side effects: Adjusting dosage or switching to alternative drugs.
In all cases, follow-up care is necessary to prevent recurrence or manage long-term effects.
Can Pinpoint Pupils Be Prevented?
While not all causes of pinpoint pupils are preventable, there are steps that can reduce the risk:
-
Use prescription medications exactly as directed.
-
Avoid exposure to unknown chemicals or unlabelled substances.
-
Seek medical advice before using any new supplements or alternative remedies.
-
If you or someone you know struggles with substance use, get support through therapy, rehabilitation, or support groups.
Being mindful of these areas can help maintain overall eye and neurological health.
Final Thoughts
A pinpoint pupil may seem like a small detail, but it can provide a big clue about what’s happening inside the body. While not always dangerous, it can be an early sign of serious issues ranging from drug overdose to brain damage. By understanding the potential causes, associated symptoms, and when to seek help, individuals can take timely action to protect their health.
- Industry
- Art
- Causes
- Crafts
- Dance
- Drinks
- Film
- Fitness
- Food
- Games
- Gardening
- Health
- Home
- Literature
- Music
- Networking
- Other
- Party
- Religion
- Shopping
- Sports
- Theater
- Wellness
- News


