Smart City Market Insights: Strategies for Success in the Urban Tech Space
Introduction
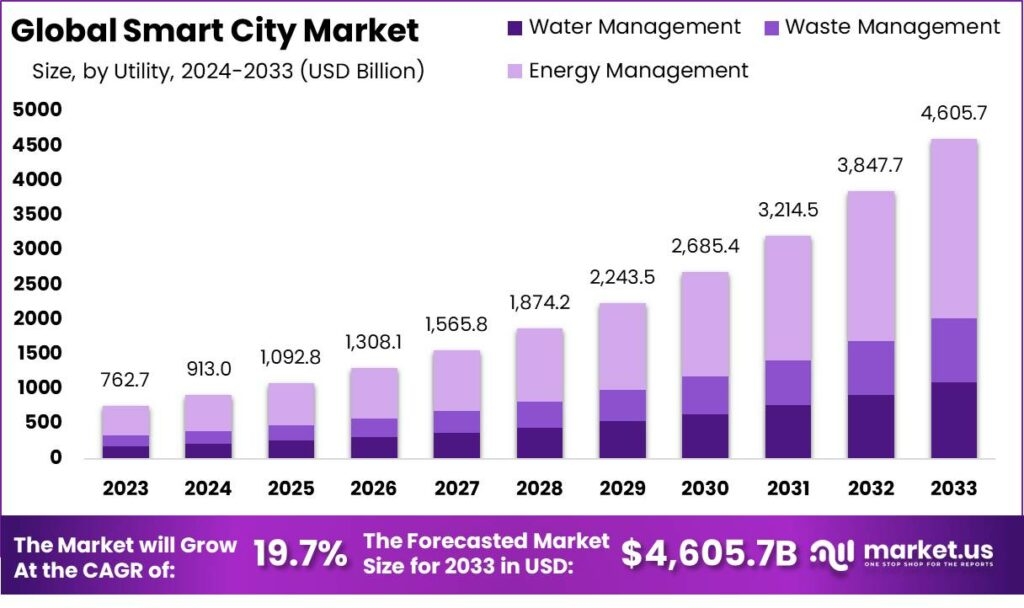
The smart city market is experiencing rapid growth driven by the increasing demand for enhanced urban infrastructure and efficiency. Factors such as the rising population, urbanization, and advancements in technology are fueling this expansion. Smart cities aim to leverage technologies like IoT, AI, and data analytics to create more connected, efficient, and sustainable urban environments.
Read More - https://market.us/report/smart-city-market/
However, challenges such as high implementation costs, data privacy concerns, and the need for substantial infrastructure upgrades pose significant hurdles. Despite these obstacles, opportunities for new entrants abound in areas like innovative tech solutions, cybersecurity, and infrastructure development, as cities seek to modernize and improve quality of life for their residents.
Emerging Trends
- IoT Integration: The Internet of Things is becoming increasingly central, connecting various city infrastructure elements to improve efficiency and data collection.
- AI and Machine Learning: These technologies are being used to optimize traffic management, energy consumption, and public safety.
- Green Technologies: There is a growing emphasis on sustainable practices, such as renewable energy sources and green building materials.
- Big Data Analytics: Cities are leveraging big data to make informed decisions and improve urban planning and management.
- Citizen Engagement Platforms: Tools and apps are being developed to enhance communication between city officials and residents, encouraging community involvement.
Top Use Cases
- Traffic Management: Smart traffic lights and sensors help reduce congestion and improve traffic flow.
- Energy Management: Smart grids and meters allow for better energy distribution and reduced waste.
- Public Safety: Surveillance systems and predictive policing tools enhance security and emergency response.
- Waste Management: Smart bins and recycling systems streamline waste collection and promote recycling.
- Water Management: Intelligent systems monitor and manage water usage and detect leaks to conserve resources.
Major Challenges
- High Costs: Implementing smart city technologies often requires significant investment, which can be a barrier for many cities.
- Data Privacy: Collecting and managing large amounts of data raises concerns about privacy and security.
- Interoperability: Integrating various technologies and systems can be complex and problematic.
- Cybersecurity Risks: As cities become more connected, they are more vulnerable to cyberattacks.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Navigating local regulations and standards can slow down the deployment of smart city solutions.
Market Opportunity
- Innovative Solutions: New technologies and startups have opportunities to address gaps in existing smart city solutions.
- Cybersecurity: There is a growing need for robust security measures to protect smart city infrastructure.
- Energy Efficiency: Solutions that enhance energy efficiency and sustainability are in high demand.
- Infrastructure Development: Opportunities exist in modernizing and expanding urban infrastructure.
- Data Analytics: Companies specializing in big data analytics can offer valuable insights for urban management.
Conclusion
The smart city market is on a dynamic growth trajectory, fueled by technological advancements and the need for more efficient urban environments. While challenges such as high costs, data privacy issues, and cybersecurity risks exist, the market also offers substantial opportunities for innovation and development.
New entrants have the chance to make a significant impact by addressing these challenges with cutting-edge solutions, contributing to the evolution of smarter, more sustainable cities.
- Industry
- Art
- Causes
- Crafts
- Dance
- Drinks
- Film
- Fitness
- Food
- Jeux
- Gardening
- Health
- Domicile
- Literature
- Music
- Networking
- Autre
- Party
- Religion
- Shopping
- Sports
- Theater
- Wellness
- News


